
- #Cobalt strike beacon set time how to
- #Cobalt strike beacon set time cracked
- #Cobalt strike beacon set time full
- #Cobalt strike beacon set time software
- #Cobalt strike beacon set time windows
#Cobalt strike beacon set time full
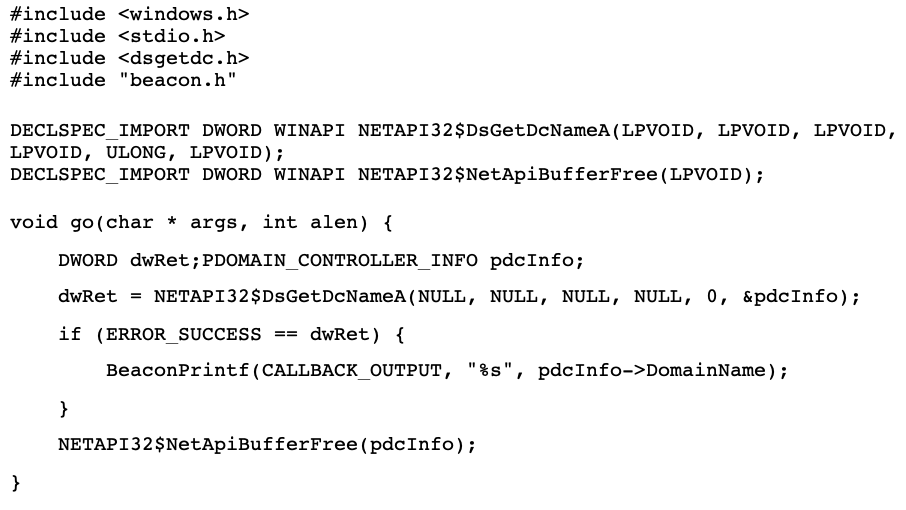
Since the goal was to make it ninja/OPSEC safe, I figured why not just do it dynamically with Assembly? About halfway through creation, I bit the bullet and burned the extra time to make it into a blog post as well, so here it is!įor the full code to the project see the GitHub repo: So that’s what I did! I created a Beacon Object File that grabs the information we’d want, right there from the beacon process memory!
#Cobalt strike beacon set time windows
I’ve been doing allot of Windows Internals studying, and this video made a lightbulb go off.This behavior of the host beacon process spawning a new whoami.exe process, triggers the EDR and the beacon is burned!.Matt uses an example where after the beacon compromises the endpoint, the first thing it does is run the whoami.exe local binary.In this talk, Matt shows how EDR heuristics can detect Cobalt Strike beacons based on their behavior.This idea was inspired by Matt Eidelberg’s DEF CON 29 talk Operation Bypass Catch My Payload If You Can. You can follow NVISO Labs on Twitter to stay up to date on all our future research and publications.This is a walkthrough of creating the Cobalt Strike Beacon Object File (BOF) “Where Am I?” You can find Didier on Twitter and LinkedIn. Didier is a SANS Internet Storm Center senior handler and Microsoft MVP, and has developed numerous popular tools to assist with malware analysis.
#Cobalt strike beacon set time how to
In upcoming blog posts, we will show in detail how to use these private keys to decrypt metadata and decrypt C2 traffic.ĭidier Stevens is a malware expert working for NVISO. This can then be used to decrypt the metadata, and the C2 traffic (more on this later). Figure 3: using option verbose to display the private key Using option verbose, the private key is also displayed. Whenever a public key is extracted with known private key, the tool highlights this: Figure 2: 1768.py extracting configuration from beaconĪt minimum, this information is further confirmation that the sample came from a rogue Cobalt Strike server (and not a red team server). This key information is now included in tool 1768.py, a tool developed by Didier Stevens to extract configurations of Cobalt Strike beacons.
Out of these 10 packages, we extracted 6 unique RSA key pairs.Ģ of these pairs are prevalent on the Internet: 25% of the Cobalt Strike servers we fingerprinted (1500+) use one of these 2 key pairs.
#Cobalt strike beacon set time cracked
Searching through VirusTotal, we found 10 cracked Cobalt Strike packages: ZIP files containing a file named.
cobaltstrike.beacon_keys? This file is not part of a legitimate Cobalt Strike package, as it is generated at first time use. One possible explanation we verified: are there cracked versions of Cobalt Strike, used by malicious actors, that include a. This implies that they use the same private key, thus that their.
#Cobalt strike beacon set time software
These keys are generated when the Cobalt Strike team server software is used for the first time.ĭuring our fingerprinting of Internet facing Cobalt Strike servers, we found public keys that are used by many different servers. Public and private keys are stored in file. RSA encryption is used to encrypt this metadata: the beacon has the public key of the C2, and the C2 has the private key. The AES key is generated by the beacon, and communicated to the C2 using an encrypted metadata blob (a cookie, by default). The communication between a Cobalt Strike beacon (client) and a Cobalt Strike team server (C2) is encrypted with AES (even when it takes place over HTTPS). We found 6 private keys for rogue Cobalt Strike software, enabling C2 network traffic decryption.
Cobalt Strike: Using Known Private Keys To Decrypt Traffic – Part 1 (current).Cobalt Strike: Using Process Memory To Decrypt Traffic – Part 3.Cobalt Strike: Using Known Private Keys To Decrypt Traffic – Part 2.Blogpost series: Cobalt Strike: Decrypting Traffic


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
